Concepts
Unitary Normalisation
Normalization of values means adjusting values measured on different scales to a notionally common scale. In this program, unitary normalisation is frequently used to convert a range of values to values between zero and one and the resulting values are used as scale values.
This following formula is used:
z = (x − min(x)) / (max(x) − min(x))
e.g. If there are a range of numbers with the lowest=50 and the highest=100, the formula will convert the lowest to 0.0 and the highest to 1.0. If another value=75, this will be converted to 0.5.
When this value is used as a scale, the highest value will have a symbol scaled by 1.0 (the largest possible) and the lowest will be scaled by 0.0 (invisible).
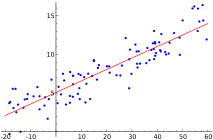
Linear Regression
Linear regression consists of finding the best-fitting straight line through the points. The best-fitting line is called a regression line.